Multi Touch Attribution
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, understanding the true impact of each marketing touch-point is crucial for optimizing campaigns and driving maximum ROI. Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) is a powerful approach that provides marketers with insights into the contributions of various marketing channels and touchpoints along the customer journey.
What is Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA)?
MTA is a methodology that aims to assign credit to multiple marketing touch-points that influence a consumer's decision-making process. It acknowledges that customer journeys are complex and rarely consist of a single touchpoint. By analyzing the complete customer journey, MTA helps marketers gain a comprehensive understanding of the relative importance and effectiveness of each marketing channel.
Understanding the Customer Journey: The customer journey is no longer a linear path from awareness to conversion. It has evolved into a dynamic and non-linear process with multiple touchpoints across various channels. MTA recognizes the complexity of these journeys and quantifies the impact of each touchpoint.
Let's consider a hypothetical online retailer, XYZ Electronics. A customer named Sarah begins her journey by clicking on a display ad showcasing the latest smartphone model. She then visits the website twice via organic search and later receives a promotional email. Finally, she converts by making a purchase through a paid search ad. To attribute credit using different models, we can represent Sarah's journey in a table:
In this example, we can see how different attribution models assign credit to each touchpoint along Sarah's journey.
Types of MTA Models:
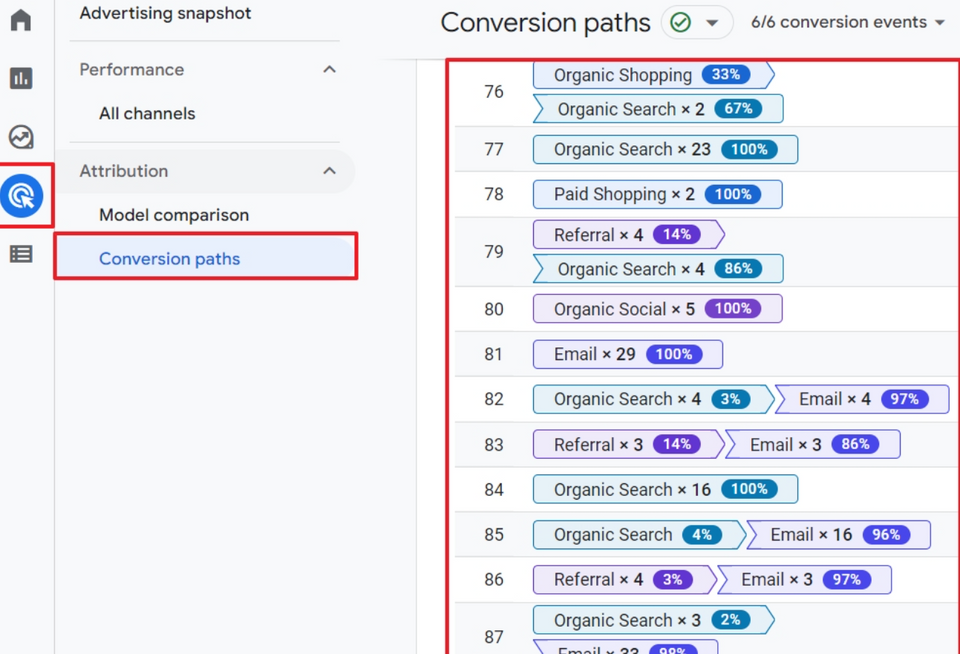
First-touch attribution model: all the credit for a conversion is assigned to the first touch-point a customer encounters. It assumes that the initial touch-point has the most significant impact on the customer's decision-making process. Using the example table:
In this model, the entire credit for the conversion would be given to the display ad since it was the first touchpoint Sarah interacted with.
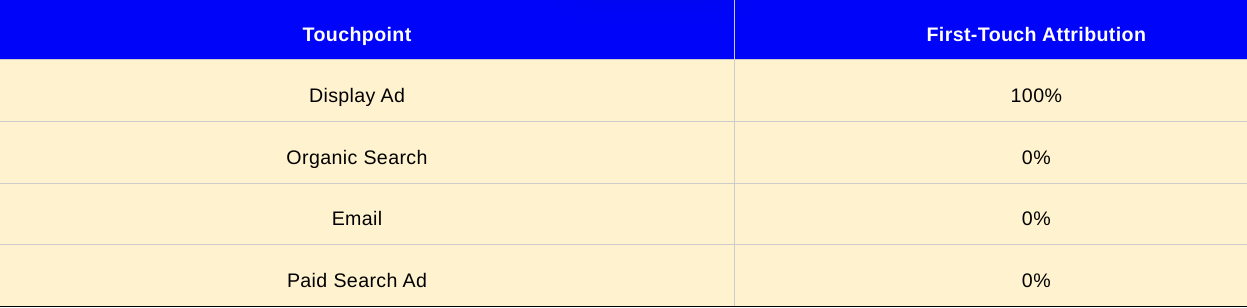
Last-Touch Attribution: In contrast to the first-touch model, last-touch attribution assigns all the credit for a conversion to the last touchpoint a customer interacts with. It assumes that the final touchpoint has the most significant influence on the customer's decision. Using the example table:
In this model, the entire credit for the conversion would be given to the paid search ad since it was the last touchpoint Sarah interacted with.
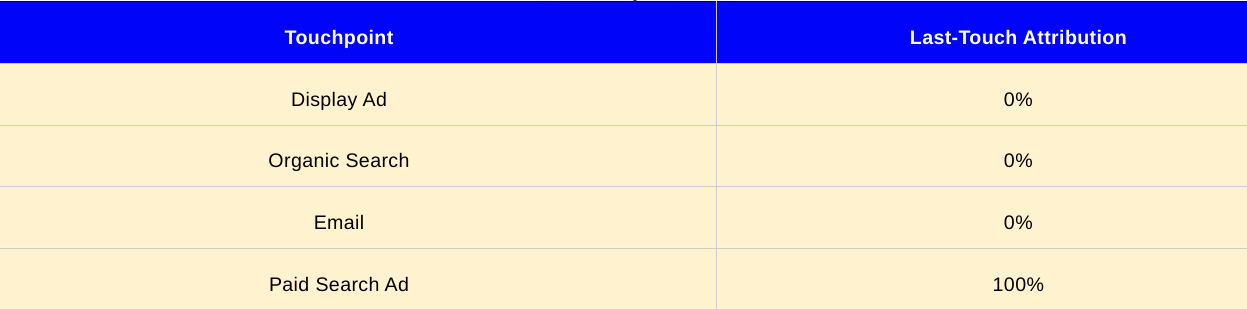
Linear Attribution: The linear attribution model distributes equal credit across all touchpoints along the customer journey. It assumes that each touchpoint contributes equally to the conversion. Using the example table:
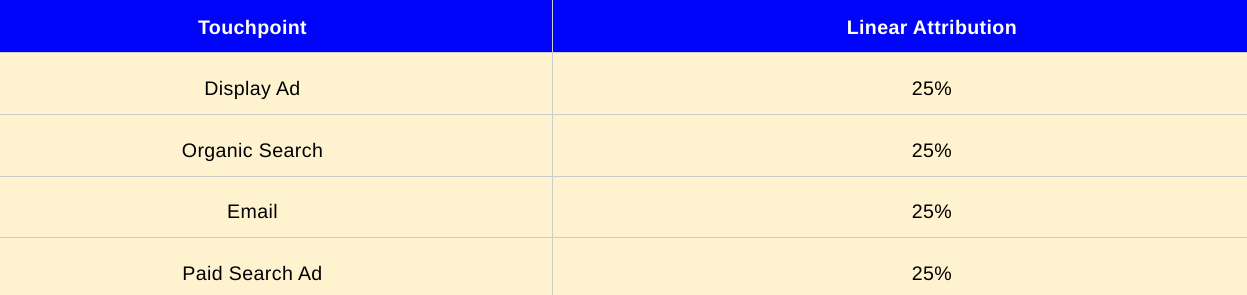
In this model, each touchpoint would receive an equal share of credit (25%) for the conversion, recognizing the contribution of each touchpoint in the customer journey.
Time-Decay Attribution: The time-decay attribution model assigns higher credit to touchpoints that occur closer to the conversion event, acknowledging that the influence of touchpoints diminishes over time. Using the example table:
In this model, the touchpoints that occurred closer to the conversion receive higher credit, while the touchpoints further back in the customer journey receive lower credit.
There are other advanced techniques —
U-Shaped Attribution: In the U-shaped attribution model, 40% of the credit is assigned to the first and last touchpoints, while the remaining 20% is evenly distributed among the touchpoints in between.
W-Shaped Attribution: In the W-shaped attribution model, 30% of the credit is assigned to the first touchpoint, last touchpoint, and specific influential touchpoints in the customer journey.
Custom Weighted Attribution: Custom weighted attribution models allow marketers to assign unique weights to each touchpoint based on their domain knowledge or specific business requirements.
Fractribution: Fractribution models utilize machine learning algorithms to assign fractional credits to individual touchpoints based on their contribution to conversions
For a highly advanced data-driven marketing professional, I would recommend adopting algorithmic attribution modeling. Algorithmic attribution models leverage advanced machine learning techniques to analyze vast amounts of data and uncover complex patterns and interactions within customer journeys. These models provide a more accurate and granular understanding of the contributions of each touchpoint, allowing marketers to make data-informed decisions and optimize their marketing strategies.
Here is an example that uses BigQuery ML engine and Linear Regression algorithm for MTA.
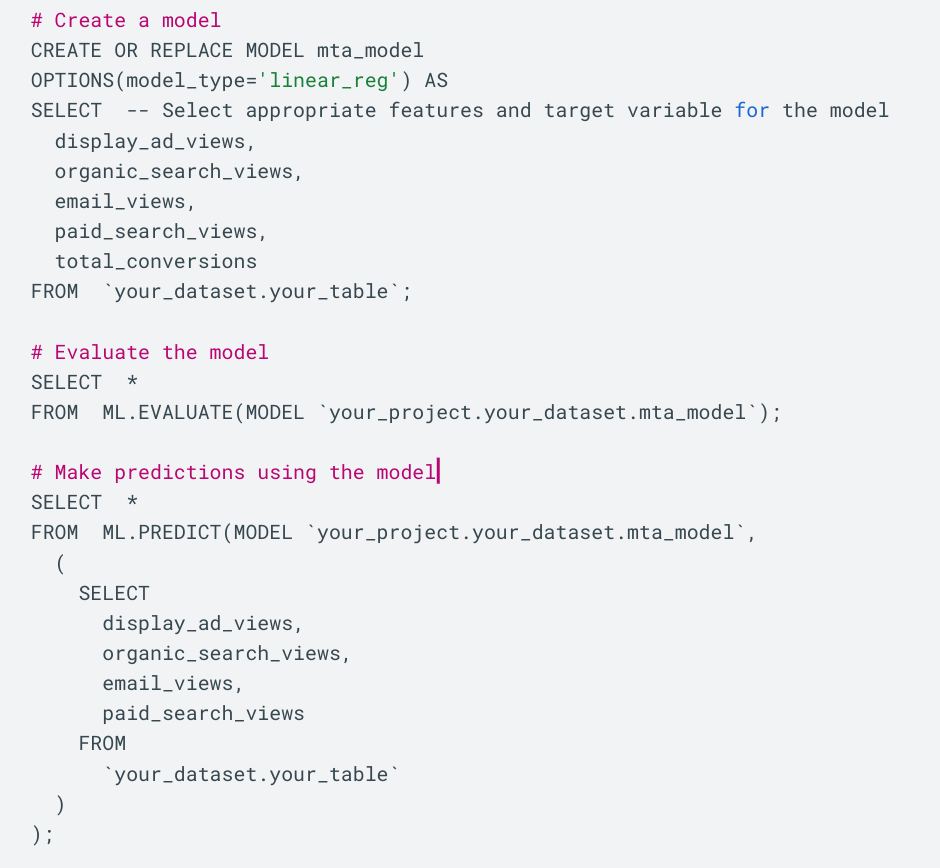
In this script, we first create a linear regression model using the specified features and the target variable (total_conversions). We then evaluate the model's performance and make predictions using the ML.EVALUATE and ML.PREDICT functions.
Conclusion: Multi-Touch Attribution empowers marketers to move beyond simplistic models and gain a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey. By adopting advanced attribution models, marketing professionals can unlock valuable insights and make informed decisions to optimize their campaigns. For data-driven practitioners proficient in data science techniques, algorithmic attribution models provide the best opportunity to harness the power of MTA. Remember, the right attribution model is the key to unlocking marketing effectiveness in a data-rich world.





Member discussion